Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of diseases that are associated with poor glucose absorption. As a result, its concentration in the blood increases significantly.
Diabetes mellitus develops for several reasons. Some types of diseases are due to a genetic predisposition, while others are related to lifestyle or environmental factors.
The disease causes significant damage to the body. A prolonged excess of glucose (sugar) in the blood gradually destroys the walls of blood vessels and can lead to dysfunction of the kidneys, heart, and death of nerve cells. But these complications can be prevented. The main thing is to follow the doctor's treatment recommendations and adjust the diet.
Types of diabetes
Depending on the mechanism of formation of pathology, two main types of diabetes mellitus are distinguished: 1st and 2nd.
In addition, there are other types of diabetes:
- potential (prediabetes), a condition in which the blood sugar level is at the upper limit of normal, but does not exceed it;
- insipidus is a disease in which the body lacks antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or the kidneys lose sensitivity to it. As a result, symptoms similar to diabetes arise: thirst, frequent urination, weakness;
- Gestational is a temporary condition that develops during pregnancy and is characterized by elevated blood glucose levels;
- latent diabetes mellitus, which develops asymptomatically for a long time (similar to type 2 diabetes), but at the same time, according to the mechanism of development, is closer to type 1 diabetes (malfunction of the immune system);
- a labile form of diabetes mellitus, in which even constant insulin therapy does not eliminate unexplained surges in blood glucose;
- a kidney disease in which the kidneys stop filtering fluid. As a result, symptoms similar to those of diabetes arise: frequent urge to urinate and a strong feeling of thirst;
- postoperative condition that develops after pancreatic surgery;
- pancreatic disease, arising against the background of chronic pathologies of the pancreas (for example, chronic pancreatitis);
- extrapancreatic disease, which occurs against the background of chronic pathologies, but can gradually lead to disruption of the pancreas.
Diabetes mellitus type 1
In this type of disease, the body's own immunity destroys the pancreatic cells that are responsible for producing insulin. As a result, insulin does not enter the blood and does not transport glucose to the cells. Because of this, it remains in the vessels and gradually destroys them.
Type 1 diabetes most often develops in children and adolescents, although it can occur at any age.
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes usually appear acutely.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes:
- intense thirst and hunger,
- weakness,
- frequent urination,
- sudden weight loss,
- blurry vision.
Without treatment, these symptoms are accompanied by signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (one of the complications of diabetes): thirst, weakness, lethargy, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, difficulty concentrating. The person may even fall into a coma.
People with type 1 diabetes take insulin for life.
Diabetes mellitus type 2

In this case, the pancreas produces enough insulin, but the cells are insensitive to it, so they cannot absorb glucose and its concentration in the blood increases.
Excess weight is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus can go unnoticed for a long time, so people do not always notice the first symptoms of the disease.
Possible symptoms of type 2 diabetes:
- frequent urination;
- be strong;
- hunger even after eating;
- fatigue;
- blurry vision;
- wounds that heal slowly;
- darkening of the skin on the elbows and knees;
- tingling, pain, or numbness in your arms and legs.
Risk of developing diabetes.
Types of diets for diabetes
There is no special diet for diabetes mellitus, but people with this diagnosis are often mistakenly advised to choose one of the strict nutritional systems that are supposed to help overcome the disease. For example, completely eliminate carbohydrates from the diet, replace them with proteins, eat only buckwheat porridge, or follow another monodiet.
No carbohydrate diet

Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for cells. There are three types: sugar, starch and fiber. Sugars are simple carbohydrates, including glucose. Natural sugars are found in fruits and vegetables, artificial (added) sugars are found in confectionery products, sauces and canned foods. Starch and fiber are complex carbohydrates. Starch is found in fruits, seeds and tubers of plants, fiber is found in fruits and vegetables, whole wheat bread and pasta.
Glucose is a carbohydrate that causes the main disorders in diabetes mellitus. Because of this, proponents of a carbohydrate-free diet believe that eliminating glucose and, at the same time, all carbohydrates from the diet will help stop the disease. This is bad.
A healthy ratio of carbohydrates in the diet is 50/55%
Carbohydrates are a source of energy, so you should not completely exclude them from your diet, and it is also quite difficult, because they are found in almost all foods.
In the absence of carbohydrates, the body begins to obtain energy from fats and proteins, the proportion of which, when following a diet of this type, usually increases due to the consumption of red meat. And this is a risk factor for heart disease and colorectal cancer.
In addition, carbohydrate sources such as fruits, vegetables and legumes contain many nutrients and minerals, the deficiency of which negatively affects health and can worsen diabetes.
High protein diet
A protein or high-protein diet is a diet in which the daily protein intake exceeds the norm (0. 8 g per 1 kg of weight) and accounts for more than 15-16% of the total calorie intake.
There is no consensus that people with diabetes need to eat more protein. However, its excess increases some health risks.
Excess protein in the diet increases the load on the kidneys and stones may begin to form in them. In addition, proteins are mainly found in meat and dairy products, so when following such a diet there is a high probability of suffering from vitamin and mineral deficiencies due to the fact that fruits and vegetables are excluded from the diet.
Buckwheat diet
The buckwheat diet is a single-product diet with strict restrictions. The diet of this diet consists of 70% buckwheat, to which other low-fat foods are gradually added: vegetables, nuts, white meat and fish.

Cereals for the buckwheat diet are prepared in a special way: they are not boiled, but poured with boiling water and left for 4-6 hours.
The main disadvantage of this diet is the limited range of foods consumed. Because of this, a person may lack beneficial vitamins and minerals. In addition, following a buckwheat diet is psychologically difficult: it may seem that nothing is allowed. Therefore, the risk of slipping and overeating high-calorie foods increases significantly.
Diet for type 1 diabetes
There is no special diet for people with type 1 diabetes, but it is important for people with this diagnosis to count the amount of carbohydrates they eat each day and take into account the glycemic index of foods. In addition, they must respect the principle or method of a healthy dish.
The amount of carbohydrates in the diet of a person with type 1 diabetes on average should not exceed 17 units of bread per day.
The amount of carbohydrates a person with diabetes can typically tolerate varies from person to person and depends on weight, physical activity level, daily caloric needs, and how the body metabolizes carbohydrates.
You can calculate the required amount of carbohydrates per day with a nutritionist or your doctor. After converting the carbohydrates you eat into units of bread, your doctor will help you determine the amount of insulin you will need to absorb the glucose. Over time, a person will learn to calculate this for himself.
Correspondence table of carbohydrate-containing products with bread units.
| Product | 1 XE (about 15g of carbohydrates) |
White bread |
1 piece |
Borodino bread |
1 piece |
Buckwheat |
1 tablespoon (dry) |
oat grains |
1 tablespoon (dry) |
| Dad | 1 medium tuber |
| Orange | 1 piece |
| Strawberry | 10 pieces |
| Apple | 1 piece |
| Milk | 1 glass |
Ice cream made with milk |
⅔ serving (without glass) |
glucose level
The glycemic index (GI) is a number that shows how the foods you eat affect your blood glucose levels.
The glycemic index is not calculated independently, it is generally indicated on food packaging.
Low GI foods are thought to slightly raise blood sugar levels and break down more slowly, so you feel full longer. High GI foods are digested faster and also significantly increase blood sugar levels.
All carbohydrate-containing products are divided into three groups:
- Low GI (from 55) skimmed milk, apples, peanuts;
- with medium GI (from 56 to 69): spaghetti, buckwheat, ice cream;
- with high GI (70 and above): white bread, rice milk, white rice.
It is useful for a person with diabetes to know the glycemic index of foods. This way you can include low GI foods in your diet and will not allow blood glucose spikes. However, other factors need to be taken into account.
Research shows that the amount of carbohydrates consumed, rather than their rate, has a greater impact on blood glucose levels. Simply put, you can also overeat apples to the point of hyperglycemia. Therefore, for most people with diabetes, the best tool to control blood glucose levels is to count carbohydrates.
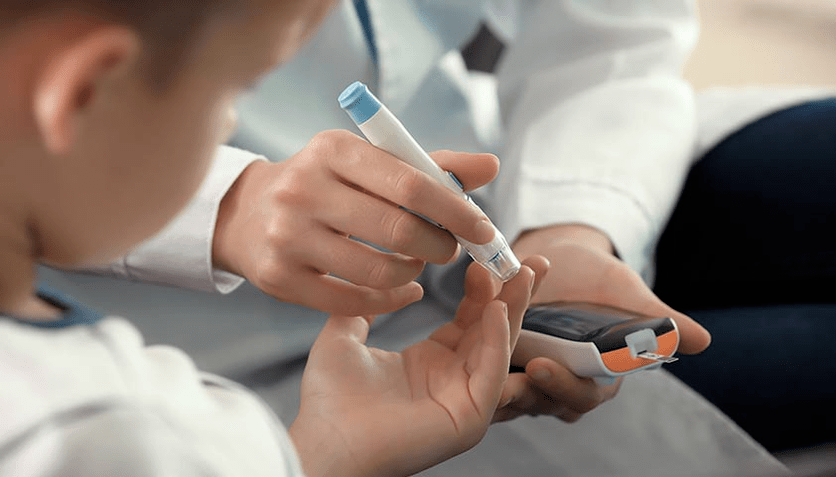
Healthy plate method
The Healthy Plate Method divides foods into five main groups: fruits and vegetables, slow-release carbohydrates, dairy, proteins and fats. You can combine these groups using a normal plate.
Fruits and vegetables should make up a third or half. Slow carbohydrates: a third or a little more. The remaining part is occupied by dairy products, a little more by protein foods and a small part by fats.
The eating principle of the healthy plate method
How to assemble a healthy dish:
- Step 1.We select a dish. Its diameter should be equal to the length of the palm.
- Step 2.Place vegetables and fruits on a plate. They can be of any form: fresh, stewed, boiled, canned. The portion should take up half the plate or a little less.
- Step 3.Divide the rest of the plate in half. In the first half we add slow carbohydrates: semi-fat products, roast potatoes, whole wheat bread or pasta. We fill the remaining quarter with protein sources: lentils, beans, peas, fish, eggs, lean meat.
Additionally, people with type 1 diabetes should follow important healthy eating principles:
- drink according to thirst;
- eat less salt, no more than a teaspoon (5-6 g) per day;
- limit the consumption of trans fats (found in many prepared and processed foods: fast food, cakes and pastries);
- Reduce the consumption of saturated fats (found in sweet pastries, fatty meats, sausages, butter and lard).
Anyone with type 1 diabetes should discuss their diet with a dietitian to determine the best nutrition and exercise plan for insulin use.
Diet for type 2 diabetes mellitus
Since foods containing carbohydrates directly affect blood sugar levels, a balanced carbohydrate diet is one of the main directions in the prevention of type 2 diabetes.
In order not to count the amount of carbohydrates eaten, doctors recommend that people with type 2 diabetes eat according to the principle of a healthy plate (as with type 1 diabetes). The diet emphasizes increasing the proportion of non-starchy vegetables, fiber and lean proteins.
In addition, this diet is rich in fiber, the consumption of which helps avoid blood sugar spikes and promotes weight loss.
Fiber is digested more slowly, which ensures a feeling of satiety for a long time.
When eating according to the healthy plate method, at each meal you should mentally divide the plate into three parts. Half should be filled with non-starchy vegetables, fresh or cooked. It could be lettuce, cauliflower, green beans, tomatoes.
A quarter of the plate should be occupied by low-fat protein sources: baked fish, boiled meat, legumes, tofu. The protein portion of the dish should fit in the palm of your hand.
The remaining quarter is complex carbohydrates such as whole wheat bread and cereals. Your portion should be the size of a fist.
Additionally, you can add a serving of healthy fat (for example, a few slices of avocado) or dress the lettuce with a tablespoon of unrefined olive oil.
Diet for gestational diabetes.
Food directly affects blood sugar levels, so a healthy and balanced diet helps control gestational diabetes and pregnancy.
There is no single correct diet that is best for women with gestational diabetes. The thing is, what works for one person may not work for another. But there are several common diets that help control the disease.
DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension)
The DASH, or Diet to Control Hypertension, was developed for people who suffer from high blood pressure. Over time, doctors and scientists discovered that this diet helps with other diseases, including gestational diabetes.
Thus, a study of 52 women with gestational diabetes found that following the DASH diet for 4 weeks led to a reduced need for insulin treatment and fewer cesarean deliveries.
According to the DASH diet, your diet should include:
- low-sodium foods (no more than 2, 300 mg of sodium per day, equivalent to 1 teaspoon of salt);
- fruit;
- vegetables;
- whole grains;
- low-fat dairy products;
- lean meats and fish;
- legumes and nuts;
- vegetable oils.
Limit consumption or exclude from the diet:
- foods high in saturated fat (red meat, full-fat dairy, coconut and palm oil);
- confectionery, sugary juices and sugary carbonated drinks, alcohol.
Mediterranean diet
The Mediterranean diet is an eating plan based on the diets of people from France, Spain, Italy, and Greece. It is made up of vegetables, fruits, protein sources, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds and olive oil.
The Mediterranean diet requires eating at least five servings of fruits and vegetables a day. One serving is 80 grams of fresh fruits and vegetables or 30 grams of dried fruits.
A serving of fruits or vegetables is, for example, a medium-sized apple, half a cup of cucumber or carrot, or a cup of leafy vegetables.
The main source of unsaturated fats in the Mediterranean diet is olive oil. Healthy fats are also found in nuts, seeds, olives and fish (mackerel, herring, sardines, tuna, salmon, trout).

With a Mediterranean diet, you should eat fish twice a week.
When following the Mediterranean diet, some foods are not eaten at all or the amount in the diet is limited. For example, you should eat red and processed meats less frequently, no more than twice a week. Dairy products are replaced with skimmed and fermented products, such as Greek yogurt or skimmed cheese.
The Mediterranean diet reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes after pregnancy. This diet is rich in fiber, which is digested slowly, prevents blood sugar swings and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Healthy plate method
Additionally, as with other types of diabetes, doctors recommend that women with gestational diabetes use the healthy plate method.
Products are divided into five main groups: fruits and vegetables, slow carbohydrates, dairy products, proteins and fats.
Using these groups you can put together your own healthy plate. Fill half the plate with vegetables, herbs and fruits, one third with slow carbohydrates (e. g. cereals, whole wheat pasta), one third with low-fat protein sources (fish, white meat, dairy products), the rest with foods healthy. vegetable fats.
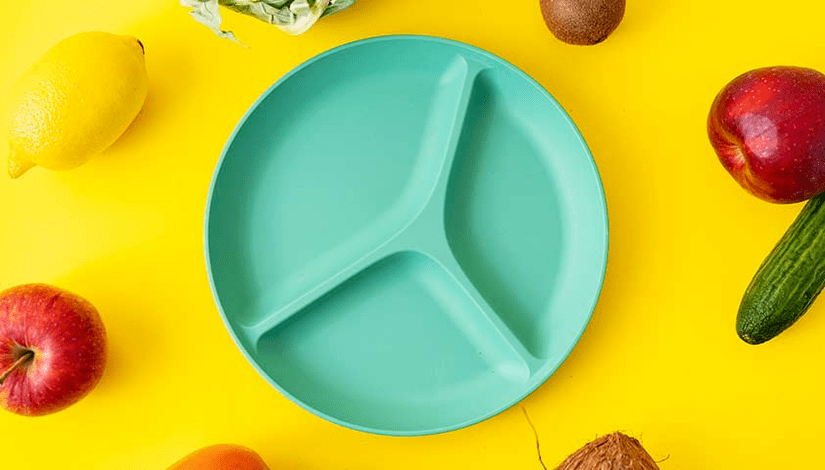

In stores you can buy plates with dividers so as not to assemble a healthy plate by eye.
Often these dishes are sold in the children's department.
Examples of diet for gestational diabetes using the healthy plate method
Breakfast:
- 1 apple,
- a handful of lettuce with a tablespoon of olive oil, ½ cucumber,
- 2 slices of whole wheat bread,
- 1 boiled egg,
- unsweetened yogurt.
Dinner:
- a serving of fermented vegetables (sauerkraut, Korean carrots);
- a handful of brown rice;
- a piece of baked white fish;
- a handful of walnuts.
Dinner:
- baked chicken breast,
- boiled green beans,
- green salad with egg,
- a few pieces of cheese.
Diet for diabetes in children.
Children often have type 1 diabetes, so they must monitor their blood sugar levels and receive insulin injections throughout their lives.
A typical school or daycare meal plan is usually very similar to what people with diabetes should follow. In the dining room they can eat everything, except products containing pure sugar: for example, it is better to replace compote with unsweetened tea or water.
Depending on what the child eats, he or her parents determine the dose of insulin needed to be administered. As a rule, the menu in canteens is prepared a week in advance, so you can know in advance what the child will eat.
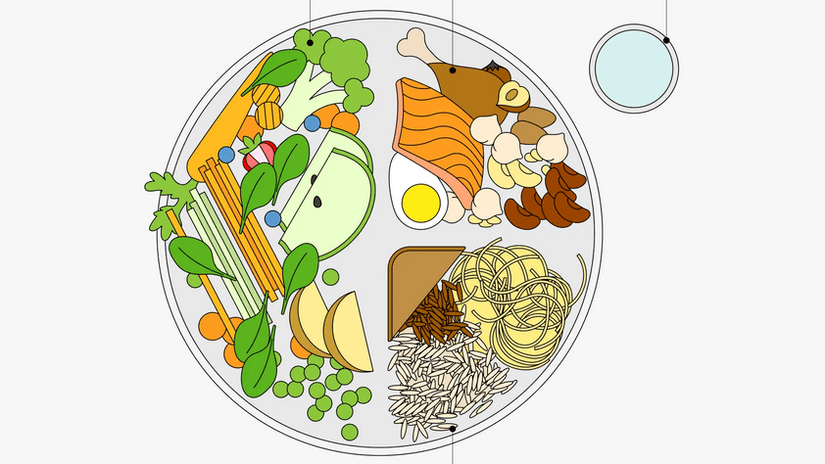
Another important condition is to ensure that the child eats snacks several times a day. This will help prevent a sharp drop in blood glucose, hypoglycemia, which can cause fainting.
Precursors of hypoglycemia: pale skin, excessive sweating, trembling hands, weakness.
A mild attack of hypoglycemia can be quickly relieved by drinking sweet juice, eating a few sugar cubes, or taking a glucose tablet. The child or parents should always have all this at hand: in a briefcase or bag.
Additionally, it is important to explain to the teacher or caregiver that the child should always have access to a snack. Preferably at the same time. And before a physical education lesson, she definitely needs to check her blood sugar level and eat something containing carbohydrates. This will help prevent a hypoglycemic attack because exercise causes the body to burn glucose faster.
Dessert recipes for people with diabetes.
People with diabetes often crave forbidden sweets, making it difficult for them to follow a healthy diet. However, there are many desserts that contain large amounts of protein and fiber and do not cause blood sugar spikes.
The carbohydrate content in all the given recipes does not exceed 15 g or 1 unit of bread. Stevia can be replaced with any regular sugar substitute.
panna cotta
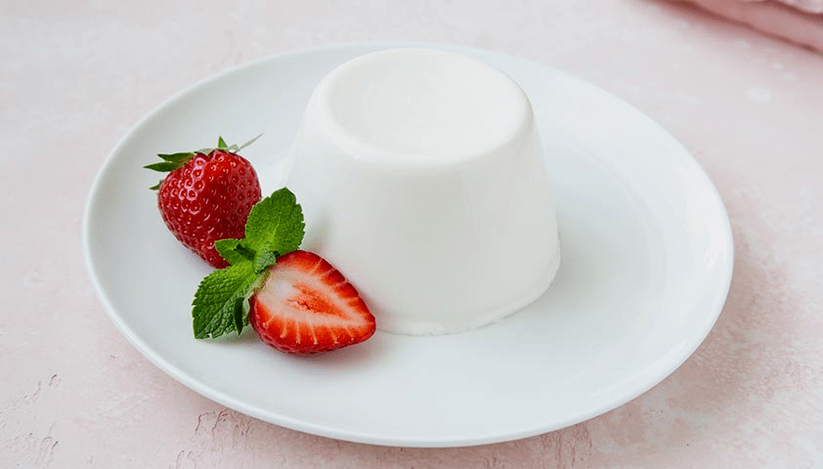

One serving of dessert contains 335 kcal, 2 g of protein, 4 g of carbohydrates, 4 g of total sugar and 0 g of added sugar.
Cooking time: 15 minutes.
The dessert must be prepared in advance because it will take time to harden after cooking (at least 3 hours).
Ingredients:
- 1, 5 tbsp. l. dry gelatin
- 60 ml cold water
- 60 ml hot water
- 2 cups heavy cream (more than 30%)
- 2 tspvanilin
- stevia to taste (about 4 g of powder)
- a pinch of salt
Preparation:
- Pour the gelatin into a bowl of cold water and let it sit for a couple of minutes. Pour in hot water and stir well until the gelatin is completely dissolved.
- Add all other ingredients and stir until smooth.
- Pour the mixture into glasses and refrigerate for at least 3 hours.
The finished panna cotta can be decorated with fresh berries.
Chocolate and peanut butter fudge
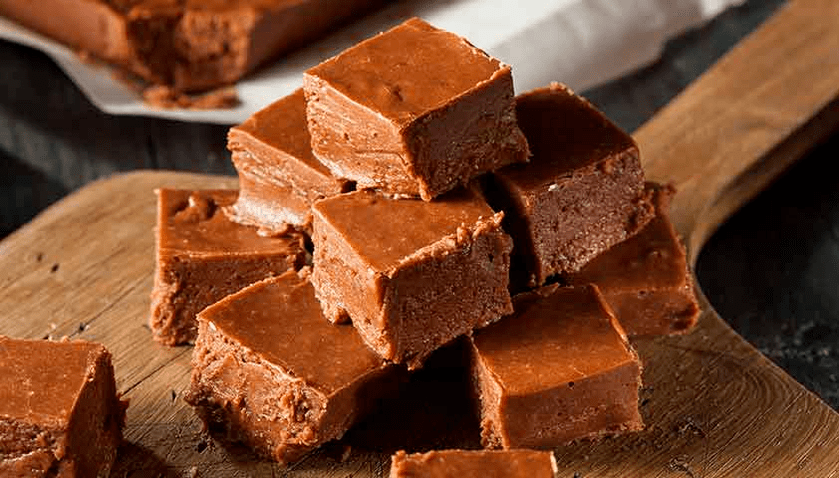

One serving of dessert contains 76 kcal, 7 g of fat, 3 g of protein, 3 g of carbohydrates, 1 g of total sugar and 0 g of added sugar.
Cooking time: 10 minutes.
Ingredients:
- 200 g dark chocolate (2 standard bars)
- 200 g unsweetened peanut butter
- 4 tspstevia powder
- ½ tspvanilin
- a pinch of salt
Preparation:
- Melt the chocolate in the microwave or in a bain-marie.
- Mix all the other ingredients with the melted chocolate.
- Pour the mixture into a silicone baking dish. Let cool to room temperature. Cut into pieces before serving.
Cheesecake and pumpkin mousse
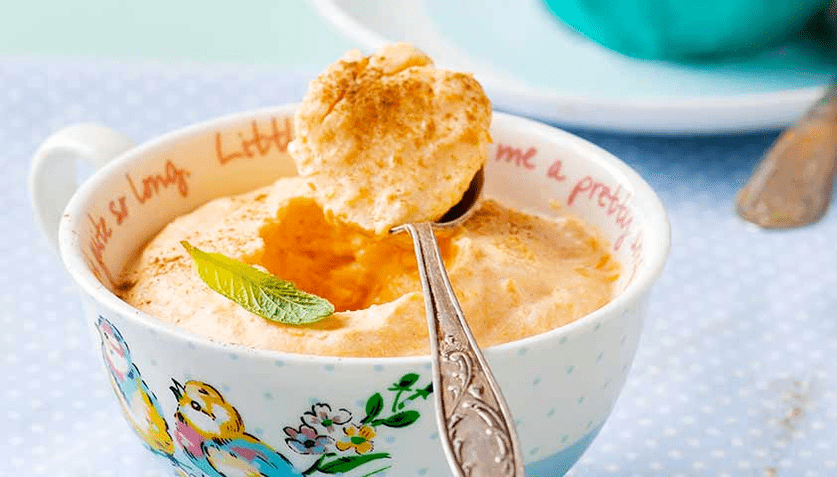

One serving of dessert contains 136 kcal, 8 g of protein, 13 g of carbohydrates, 2 g of fiber, 8 g of total sugars and 5 g of added sugars.
Cooking time: 30 minutes.
Ingredients:
- 150 g pumpkin puree
- 150 g low-fat cottage cheese or ricotta
- 1, 5 tbsp. l. honey or maple syrup
- ½ tspcinnamon
- ½ tspvanilin
- a pinch of salt
- 50 grams of Greek yogurt
- Almond flakes to decorate
Preparation:
- Blend pumpkin puree, cottage cheese, honey, cinnamon, vanilla and salt until smooth.
- Cover the glass with the resulting mixture with a lid or plastic wrap and place it in the refrigerator for 30 minutes.
- Before serving, divide the mixture into glasses, decorate with yogurt and almond petals.
Popcorn with cinnamon and apple
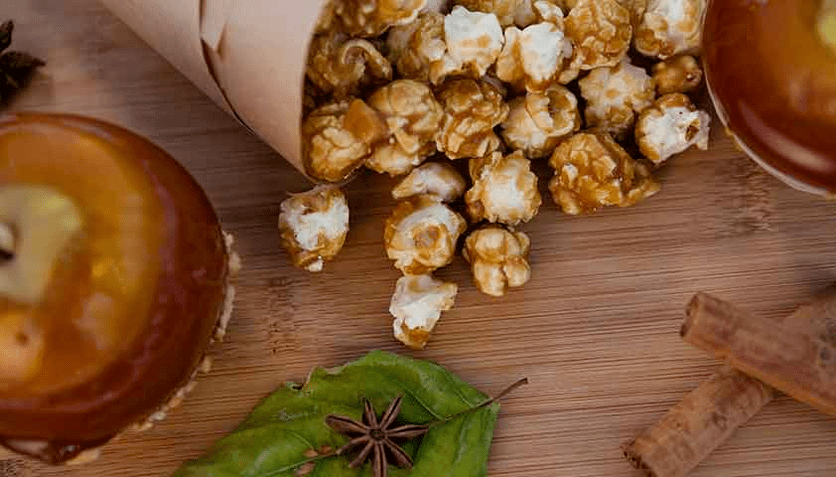

One serving of dessert contains 154 kcal, 9 g of fat, 2 g of protein, 15 g of carbohydrates, 3 g of fiber, 5 g of total sugar and 0 g of added sugar.
Cooking time: 10 minutes.
Ingredients:
- 1 tablespoon. l. olive oil
- 2 tablespoons. l. dried popcorn kernels
- ¾ tsp. cinnamon
- 100 g dried apples
Preparation:
- Heat the oil in a small skillet over medium heat.
- Place 1 or 2 popcorn kernels in the pan. Once they pop, you can pour in the remaining popcorn.
- Cover the pan with a lid and wait until all the kernels open. Shake the pan occasionally.Carefully!Do not open the lid until the popcorn has cooled because hot oil or kernels may burn your skin.
- Sprinkle the finished popcorn with cinnamon and apple slices.
gogol-mughal
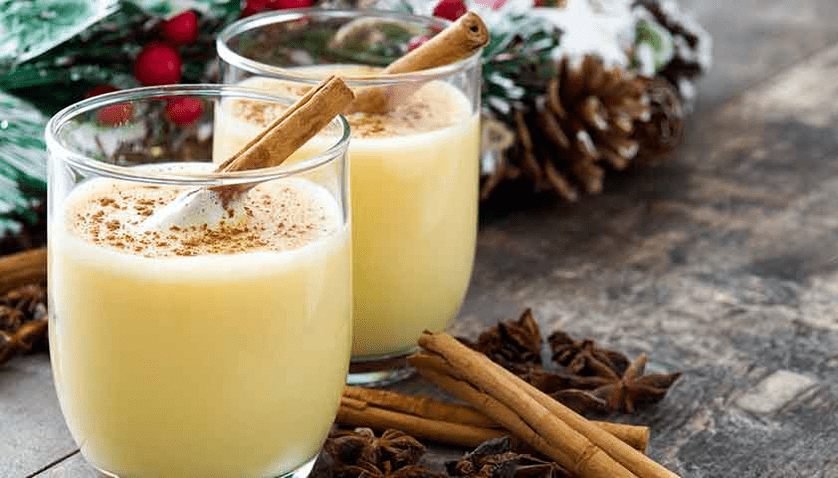

One serving of dessert contains 155 kcal, 9 g of fat, 6 g of protein, 6 g of carbohydrates, 6 g of total sugar and 0 g of added sugar.
Cooking time: 15 minutes.
Ingredients:
- 6 medium eggs
- 5. 5 cups whole milk
- 0. 5 cups heavy cream (more than 30%)
- stevia to taste (about 4 g of powder)
- a pinch of cinnamon and nutmeg
Preparation:
- Place all ingredients except nutmeg in a blender and blend until smooth.
- Pour the mixture into glasses and sprinkle with nutmeg.
The finished eggnog can be decorated with a cinnamon stick.